Hormonal Imbalance: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments
Hormonal Imbalance: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments

Hormones are essential chemical messengers in the human body, regulating various physiological processes such as growth, metabolism, mood, and reproduction. Hormonal balance is crucial for overall health and well-being. However, hormonal imbalances can occur for a variety of reasons, leading to a range of symptoms and health issues. In this guide, we will explore the causes of hormonal imbalance, their symptoms, and the effective treatments available to restore hormonal equilibrium.
I. Causes of Hormonal Imbalance
-
Age-Related Changes
Aging is a natural process that can lead to hormonal imbalances. Both men and women experience age-related changes in hormone levels. For women, menopause typically occurs in their late 40s or early 50s, resulting in a decline in estrogen and progesterone levels. In men, andropause, characterized by a reduction in testosterone production, is a common hormonal change that occurs with age.
-
Stress
Stress is a significant contributor to hormonal imbalances. The body’s response to stress triggers the release of cortisol, the primary stress hormone. Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, disrupting the balance of other hormones such as insulin, thyroid hormones, and reproductive hormones. This disruption can manifest in various health problems.
-
Poor Diet and Nutrition
Diet plays a crucial role in hormone regulation. An unhealthy diet high in processed foods, sugar, and trans fats can lead to insulin resistance, affecting blood sugar levels. Additionally, inadequate intake of essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids can disrupt hormone production and balance.
-
Lack of Physical Activity
Physical activity is essential for maintaining hormonal balance. Regular exercise helps to regulate insulin sensitivity and encourage the proper function of various hormones. A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other hormonal imbalances.
-
Obesity
Obesity is closely linked to hormonal imbalances. Excess body fat, especially in the abdominal region, can lead to increased production of insulin and estrogen. These imbalances can contribute to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and metabolic syndrome.
-
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can disrupt hormonal balance. Examples include thyroid disorders (hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism), diabetes, and pituitary gland disorders. These conditions can impact the secretion and regulation of hormones, leading to various symptoms and complications.
-
Medications
Certain medications can interfere with the body’s hormone levels. For instance, birth control pills, corticosteroids, and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can affect estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones. Patients on such medications should be monitored regularly by healthcare professionals to assess and address any hormonal imbalances.
-
Environmental Toxins
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as endocrine-disrupting chemicals, can influence hormonal balance. These substances are found in various everyday products, including plastics, pesticides, and some cosmetics. They can interfere with the endocrine system’s normal functioning and lead to hormonal imbalances.
-
Genetics
Genetic factors can predispose individuals to hormonal imbalances. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which affects hormone regulation in women, have a genetic component. Understanding one’s genetic predisposition can be essential for addressing and managing hormonal imbalances effectively.

II. Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance
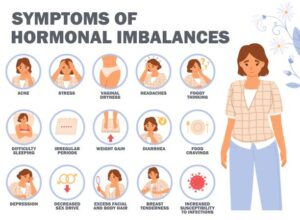
Hormonal imbalances can manifest in a wide range of symptoms, affecting various aspects of health and well-being. The specific symptoms may vary depending on the hormones involved and the severity of the imbalance. Here are some common symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances:
-
Irregular Menstrual Cycles
Hormonal imbalances in women often lead to irregular menstrual cycles. This can include missed periods, heavy or prolonged bleeding, and other menstrual irregularities. Conditions like PCOS and endometriosis can exacerbate these symptoms.
-
Mood Swings and Emotional Changes
Hormones play a significant role in regulating mood and emotions. Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone can lead to mood swings, anxiety, and depression. For example, premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is characterized by emotional symptoms related to hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle.
-
Weight Gain or Loss
Hormonal imbalances can affect metabolism and lead to weight changes. Insulin resistance, thyroid dysfunction, and imbalances in leptin and ghrelin (hunger-regulating hormones) can contribute to weight gain or loss.
-
Fatigue and Low Energy
Imbalances in cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, can result in fatigue and low energy levels. Chronic stress and adrenal fatigue are often associated with these symptoms.
-
Hair and Skin Changes
Hormonal imbalances can affect hair and skin health. Conditions like androgenetic alopecia, caused by imbalances in androgens (male hormones), can lead to hair loss in both men and women. Acne, oily skin, and dry skin are also common skin issues related to hormonal fluctuations.
-
Insomnia and Sleep Disturbances
Melatonin, a hormone responsible for regulating the sleep-wake cycle, can be disrupted by hormonal imbalances. This disruption may result in insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, or disrupted sleep patterns.
-
Digestive Problems
Hormonal imbalances can impact the digestive system, leading to symptoms like bloating, constipation, or diarrhea. Imbalances in insulin and cortisol can affect appetite and digestion.
-
Libido Changes
Sexual desire and libido can be influenced by hormonal imbalances. Conditions such as low testosterone in men and imbalances in estrogen and progesterone in women can lead to changes in sexual desire and function.
-
Joint and Muscle Pain
Hormonal imbalances may contribute to joint and muscle pain. Conditions like fibromyalgia are often associated with hormonal fluctuations and can result in chronic pain.
-
Changes in Blood Sugar Levels
Insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, can be disrupted by hormonal imbalances. This can lead to symptoms such as hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) in individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
-
Cognitive Impairment
Hormonal imbalances can affect cognitive function, leading to memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and mental fogginess. Hormones such as thyroid hormones and estrogen play critical roles in brain function.
-
Changes in Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Hormonal imbalances can influence heart rate and blood pressure. Conditions like hyperthyroidism, characterized by excess thyroid hormone production, can result in an increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure.
It is important to note that hormonal imbalances can affect individuals differently, and the severity of symptoms can vary. Additionally, some symptoms may overlap with multiple hormonal imbalances, making diagnosis and treatment more complex.

III. Diagnosis of Hormonal Imbalance
Diagnosing hormonal imbalances requires a thorough medical evaluation and may involve multiple steps. A healthcare provider will typically follow these procedures to determine the nature and extent of the hormonal imbalance:
-
Medical History
Taking a detailed medical history is the initial step in identifying hormonal imbalances. The healthcare provider will ask questions about the patient’s symptoms, their duration, and any underlying health conditions.
-
Physical Examination
A physical examination can provide valuable information about the patient’s overall health and may reveal signs of hormonal imbalances. For example, examining the skin, hair, and nails can help identify dermatological symptoms.
-
Blood Tests
Blood tests are crucial for assessing hormone levels. Specific hormones are measured to identify imbalances. Commonly tested hormones include thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4), sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone), insulin, cortisol, and others.
-
Imaging Studies
In some cases, imaging studies may be necessary to identify structural issues or abnormalities in the endocrine system. For instance, ultrasounds, MRIs, or CT scans can help visualize the thyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs.
-
Additional Testing
Depending on the specific symptoms and suspected hormonal imbalances, additional tests may be required. For example, a glucose tolerance test can help diagnose insulin resistance, while a bone density scan may be necessary to evaluate bone health in individuals with hormonal imbalances related to calcium and vitamin D regulation.
-
Hormone Challenges
In certain situations, hormone challenges or stimulation tests may be performed to assess the body’s response to specific hormones. For instance, the insulin tolerance test can help diagnose growth hormone deficiency.
Once a hormonal imbalance is diagnosed, the healthcare provider will work with the patient to develop a tailored treatment plan. Treatment strategies will vary depending on the nature and cause of the hormonal imbalance.

IV. Treatment of Hormonal Imbalance
The treatment of hormonal imbalances aims to restore hormone levels to their normal range and alleviate associated symptoms. The specific treatment approach will depend on the type of hormonal imbalance, its underlying cause, and the individual’s health and preferences. Here are some common treatment options for hormonal imbalances:
Lifestyle Modifications
For many individuals, making positive lifestyle changes can help correct hormonal imbalances or manage symptoms effectively. These modifications may include:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a nutritious diet that includes whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables can support hormone regulation. Reducing sugar and processed foods is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce stress, and promote hormonal balance. Both cardiovascular and strength training exercises can be beneficial.
- Stress Management: Learning to manage and reduce stress is essential for hormonal balance. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and mindfulness, can be helpful.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for hormonal health. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night to support hormone regulation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance, especially in cases of obesity-related hormonal imbalances.
- Avoiding Environmental Toxins: Reducing exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals can help maintain hormonal balance. This includes choosing natural and organic products whenever possible.
Natural Remedies
Many individuals seek natural remedies to support hormonal balance. While these approaches may not be a primary treatment, they can complement medical interventions and promote overall well-being. Some natural remedies include:
Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, such as chaste berry, black cohosh, and maca, are believed to have hormone-balancing properties. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using these supplements.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture may help balance hormones and alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances.
Dietary Supplements: Vitamins and minerals like vitamin D, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids play a role in hormonal regulation. Ensuring adequate intake of these nutrients through supplements or diet can be beneficial.
Essential Oils: Some essential oils, like lavender and clary sage, are thought to have calming effects that may help reduce stress and support hormonal balance when used in aromatherapy.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to address hormonal imbalances. The type of medication will depend on the specific hormonal issue and its underlying cause. Common medications include:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): HRT is often used to address menopausal symptoms in women. It involves replacing estrogen and sometimes progesterone to alleviate symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and vaginal dryness.
- Thyroid Medications: For individuals with thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, thyroid hormone replacement medications are prescribed to restore normal thyroid function.
- Insulin-Sensitizing Medications: Individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes may be prescribed medications that enhance insulin sensitivity, such as metformin.
- Birth Control Pills: Birth control pills can help regulate hormone levels and manage symptoms in conditions like PCOS and endometriosis.
Hormone Therapy
For certain hormonal imbalances, hormone therapy may be recommended to restore balance. This can include the use of hormones such as testosterone or growth hormone to address deficiencies. Hormone therapy should be closely monitored by a healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy.
Surgery
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to correct hormonal imbalances. Surgical options may include:
- Oophorectomy: The removal of one or both ovaries may be recommended in cases of severe hormone-related conditions, such as ovarian cancer or endometriosis.
- Thyroid Surgery: Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary in cases of thyroid cancer or severe hyperthyroidism.
- Adrenalectomy: The removal of one or both adrenal glands may be required in cases of adrenal tumors or certain hormone-related conditions.
Surgical interventions are typically considered when other treatment options are ineffective or when there is a clear medical indication for the procedure.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Many individuals seek alternative and complementary therapies to address hormonal imbalances. These therapies may include acupuncture, herbal supplements, chiropractic care, and naturopathic medicine. While some people report benefits from these approaches, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using them and to ensure they are used in conjunction with evidence-based medical treatments.
Psychological Support
Hormonal imbalances can have a significant impact on mental health. It’s important to address the emotional and psychological aspects of hormonal imbalance. Psychotherapy, counseling, and support groups can provide valuable tools for managing the emotional challenges associated with hormonal imbalances.
Conclusion
Hormonal imbalances are common and can affect individuals of all ages and genders. Understanding the causes and symptoms of hormonal imbalances is the first step toward effective diagnosis and treatment. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific hormonal issues and underlying causes. By making lifestyle modifications, considering medications or hormone therapy when necessary, and seeking alternative therapies when appropriate, individuals can regain hormonal balance and improve their overall health and well-being. Whether it’s through traditional medicine or complementary approaches, restoring hormonal equilibrium can lead to a happier and healthier life.





